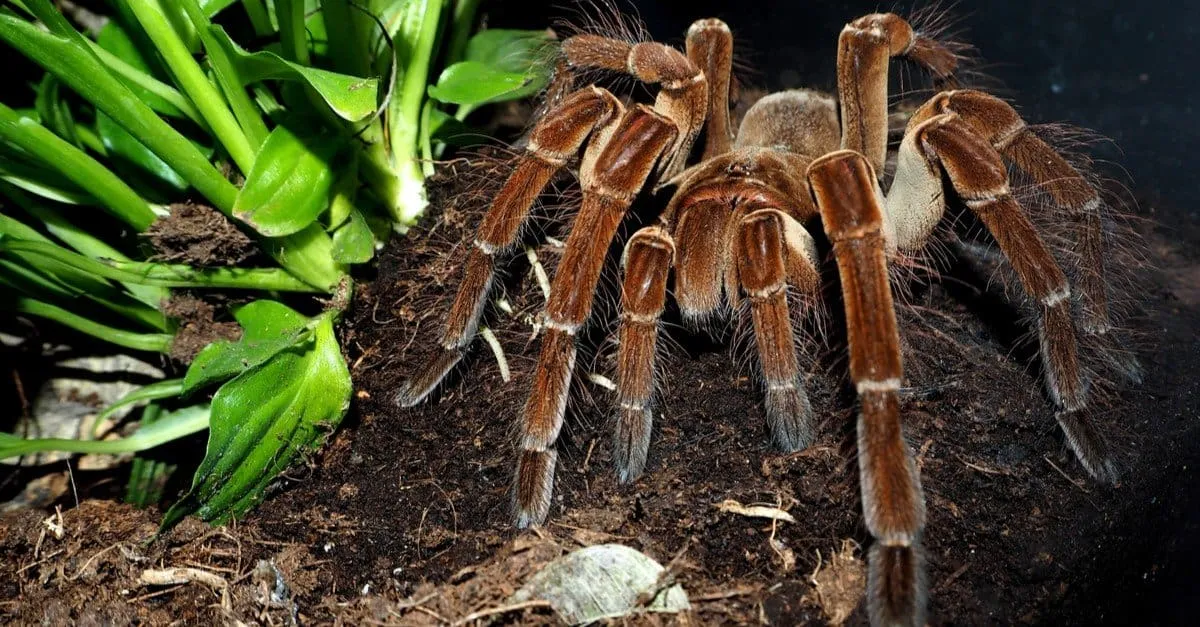
What is a Goliath Birdeater Tarantula?
The Goliath Birdeater Tarantula (Theraphosa blondi) is a giant spider native to the rainforests of northern South America. This impressive arachnid holds the title of the world’s largest spider by mass and can be a fascinating, if intimidating, subject of study. Known for its size, impressive fangs, and unique behaviors, the Goliath Birdeater is a remarkable creature that has captured the attention of scientists, enthusiasts, and anyone interested in the wonders of the natural world. Their sheer size is one of the most astonishing facts about them, making them stand out among other spiders. They are a prime example of the biodiversity found in the Amazon rainforest and surrounding areas.
Physical Characteristics
The Goliath Birdeater Tarantula boasts a suite of physical attributes that contribute to its imposing presence and survival in its natural habitat. Their size is, of course, the most striking feature, but there’s much more to appreciate about these arachnids. From their hairy bodies to their powerful fangs, every aspect of their anatomy serves a specific purpose. Observing their features helps in understanding how they’ve adapted to thrive in their environment. These characteristics aren’t just for show; they are essential for their survival and how they interact with the world.
Size and Appearance
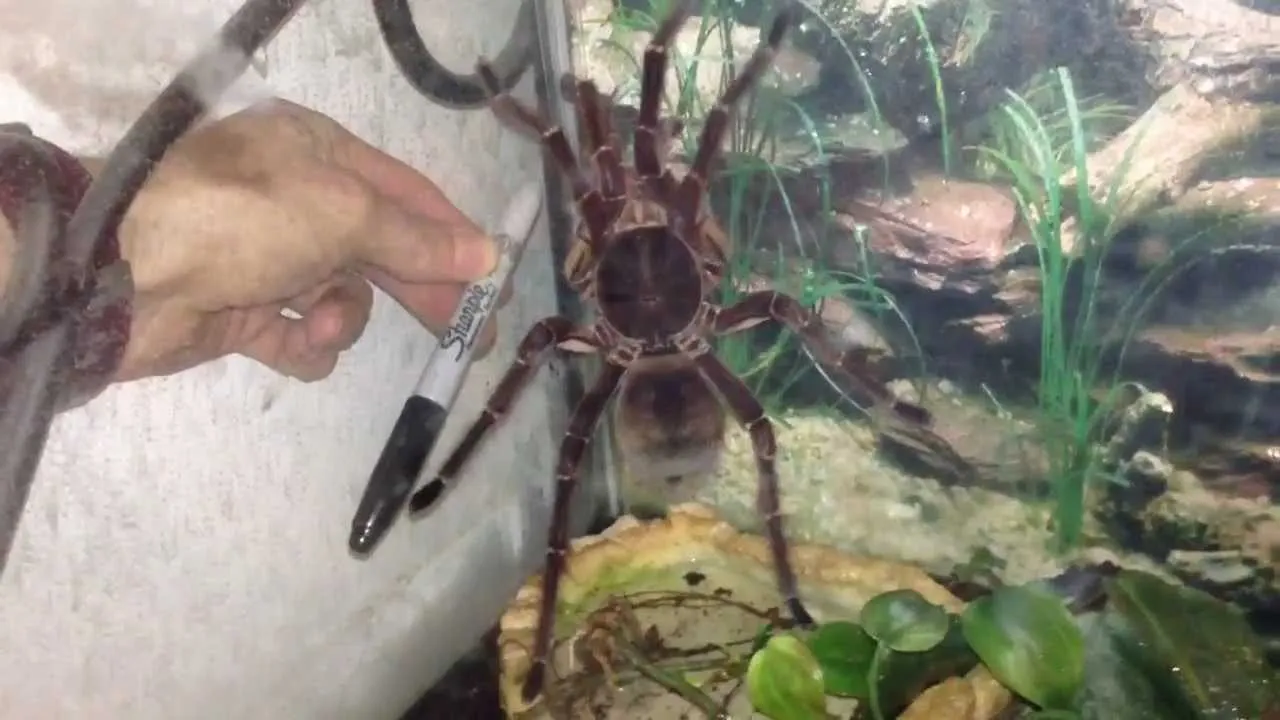

As the name suggests, the Goliath Birdeater is massive. With a leg span that can reach up to 12 inches (30 cm) or more, they are truly giants in the spider world. Their body length can be up to 4 inches (10 cm). They are also incredibly heavy, with mature females often weighing more than 6 ounces (170 grams). This significant size makes them easily recognizable and a visual spectacle. Their impressive size is not just about bulk; it also plays a critical role in their hunting strategy and ability to dominate their environment. (Image goliath-birdeater-size-comparison.webp)
Coloration and Markings
The Goliath Birdeater’s coloration is generally a dark brown, sometimes with a slight reddish hue. Their bodies are covered in dense, reddish-brown hairs, which contribute to their formidable appearance. The hairs serve a sensory function, helping them detect vibrations, and also act as a defense mechanism. These hairs can be flicked off in a stinging manner, irritating potential predators. The overall appearance provides excellent camouflage in their forest habitat, allowing them to blend in with the leaf litter and forest floor. This effective camouflage plays a key role in their ambush hunting tactics.
Habitat and Distribution
The Goliath Birdeater is exclusively found in the rainforests of northern South America. They inhabit the humid, tropical environments of countries such as Brazil, Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana. Their habitat is characterized by dense vegetation, high humidity, and a warm climate, which provides the perfect conditions for these spiders to thrive. The distribution is limited to these specific geographical regions, adding to their mystique and the importance of conservation efforts to protect their natural environment. (Image goliath-birdeater-in-habitat.webp)
Where Goliath Birdeaters Live
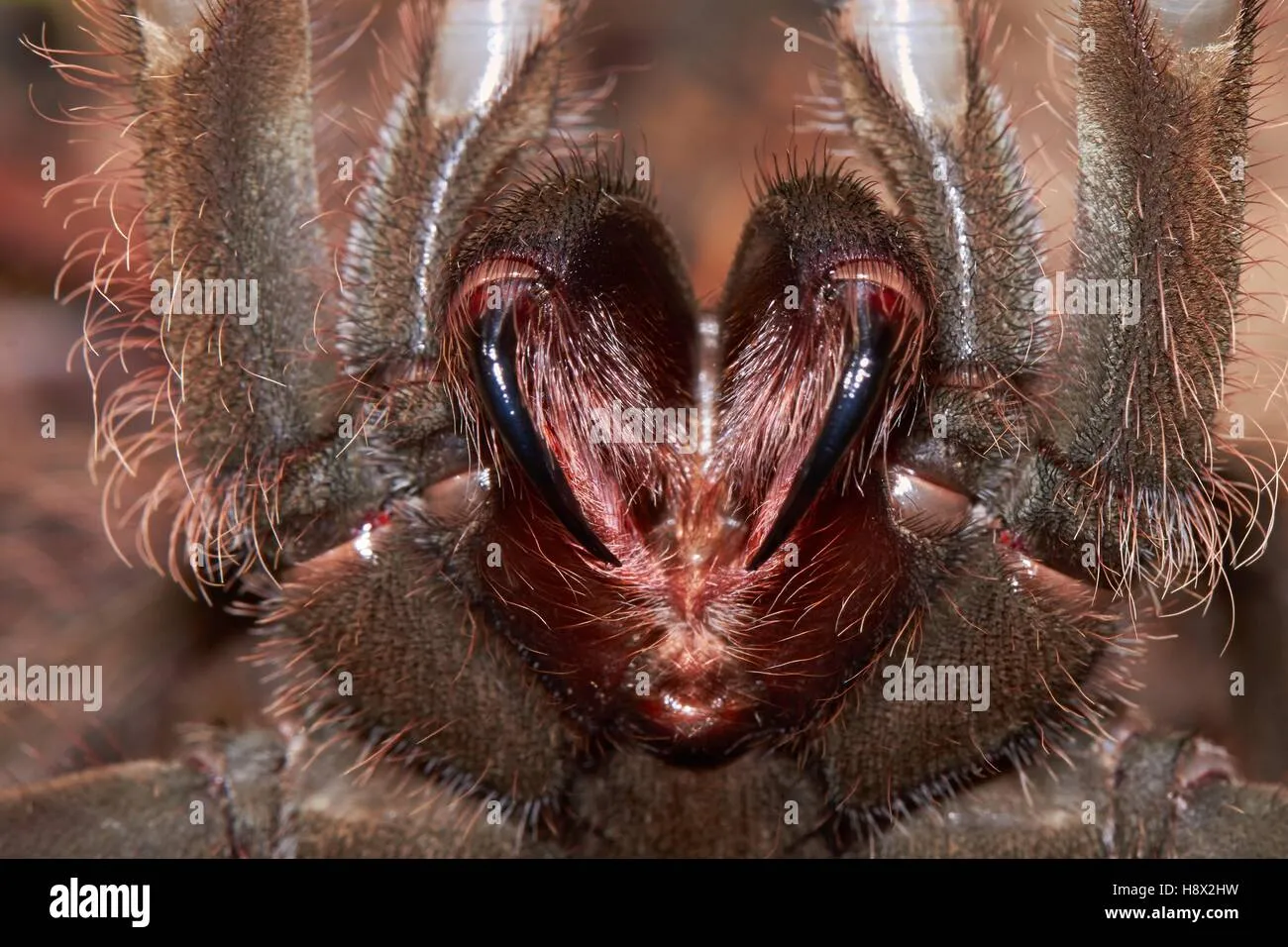
Goliath Birdeaters live in burrows, typically found in the earth or under rocks and tree roots. These burrows provide a safe haven from predators and the elements. They are often constructed in areas with moist soil, which is ideal for maintaining the required humidity levels. The spiders may also utilize natural crevices and cavities, adapting their homes to suit the immediate environment. Their preference for specific living conditions makes them somewhat sensitive to habitat destruction and environmental changes.
Natural Environment
The natural environment of the Goliath Birdeater is characterized by dense rainforest vegetation, a warm and humid climate, and the presence of other wildlife. They often share their environment with other invertebrates, small mammals, and various bird species. The rich biodiversity of their habitat provides a diverse food supply, which includes insects, worms, and occasionally small vertebrates. Preserving their natural environment is crucial for ensuring the survival of this remarkable species and maintaining the ecological balance of the rainforest.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Contrary to their name, Goliath Birdeaters rarely consume birds. However, their diet is still impressive and varied, reflecting their opportunistic nature. Their hunting behavior is a combination of patience, stealth, and impressive predatory skills. Understanding their diet is important to understand their role in the ecosystem and what needs to be done to protect them. Their feeding habits also provide insight into their overall health and well-being.
What Goliath Birdeaters Eat
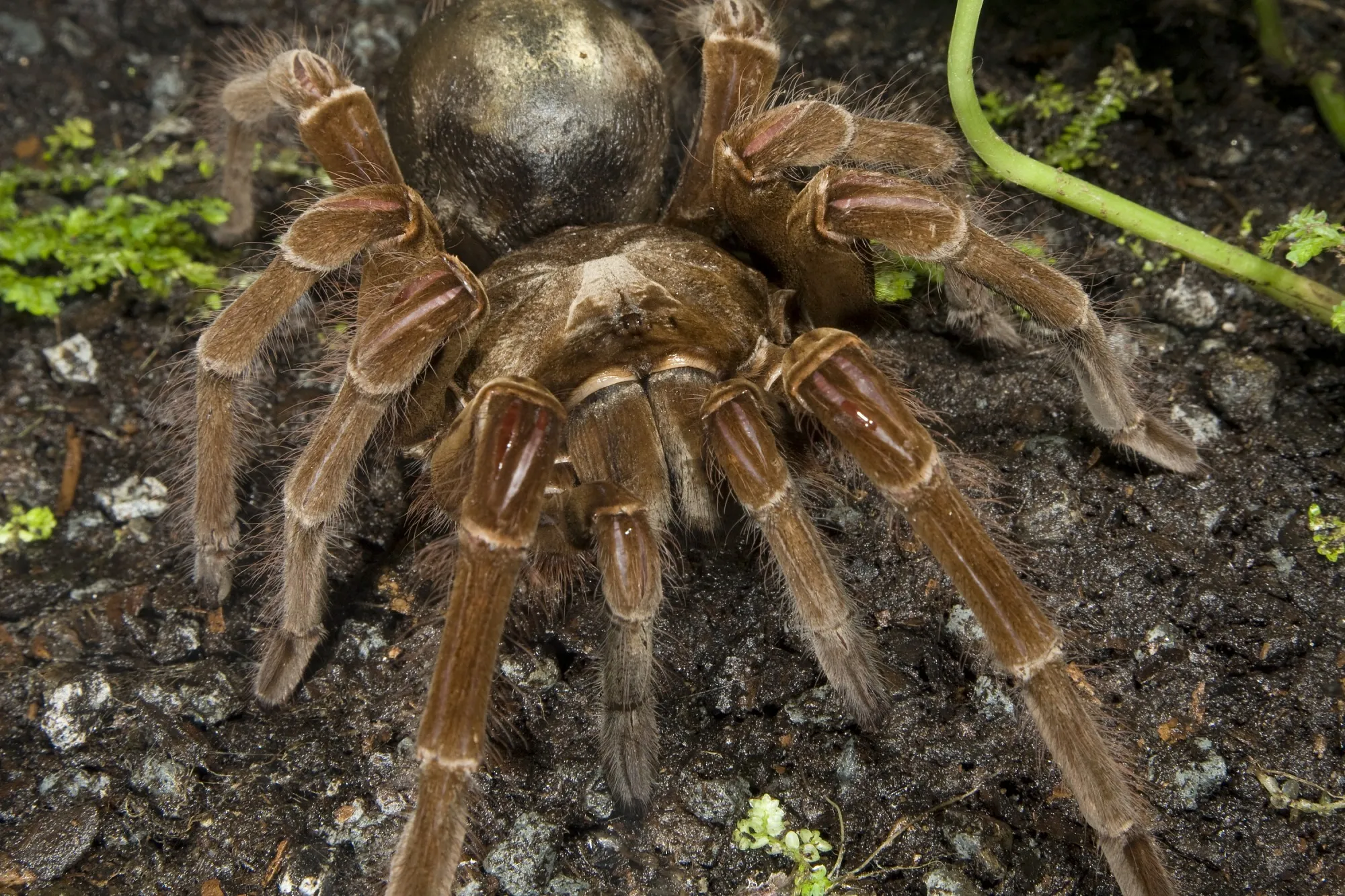

The Goliath Birdeater’s diet primarily consists of insects, worms, and other invertebrates. They are ambush predators, waiting patiently for their prey to come within striking distance. They will also consume small vertebrates, such as lizards, frogs, and, on rare occasions, small birds. Their diet is opportunistic, meaning they will eat whatever is available and can be caught. Their powerful fangs and venom help them to subdue and consume their prey effectively. (Image goliath-birdeater-eating.webp)
Hunting and Predatory Behavior
Goliath Birdeaters are ambush predators, meaning they wait for prey to come within reach before striking. They use their sensitive hairs to detect vibrations in the ground, alerting them to the presence of potential meals. Once prey is close enough, they lunge forward with incredible speed, injecting venom through their fangs to paralyze the victim. They then use their chelicerae (fang-bearing mouthparts) to crush and consume their prey. Their hunting behavior is a remarkable display of stealth and precision.
Behavior and Temperament
The Goliath Birdeater Tarantula is known for its generally docile nature, although it can be defensive if threatened. Understanding their behavior and temperament is crucial for anyone interacting with these spiders. Their behavior in the wild is influenced by factors such as habitat, food availability, and potential predators. Recognizing their behavioral patterns and temperaments is essential for responsible animal care and conservation efforts. Their personalities can vary from individual to individual, and their actions are heavily influenced by their environment and how they’ve been treated.
Handling and Interaction
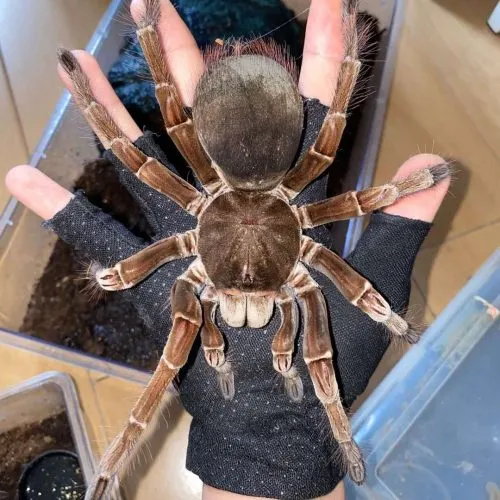

Handling a Goliath Birdeater Tarantula is generally not recommended for novice enthusiasts. Due to their size and potential defensive behaviors, it is best to admire them from a distance. If handling is necessary, it should be done with extreme caution and expertise. The spiders can flick urticating hairs as a defense mechanism, causing irritation to the skin and eyes. Handling requires a thorough understanding of their behavior and potential risks, along with the appropriate safety equipment. It is important to prioritize the spider’s well-being and avoid unnecessary stress.
Defensive Mechanisms
The Goliath Birdeater has several defensive mechanisms to protect itself from predators. Their primary defense is their urticating hairs, which they flick off their abdomen when threatened. These hairs cause intense irritation and itching upon contact. In addition to the hairs, they have large fangs and can deliver a painful bite. They also tend to retreat into their burrows if they feel threatened. Understanding these mechanisms provides valuable insight into their survival strategies and the delicate balance between defense and vulnerability. (Image goliath-birdeater-defensive-pose.webp)
Lifespan and Life Cycle
The Goliath Birdeater Tarantula has a relatively long lifespan, especially for a spider. Understanding the stages of their life cycle, from molting to reproduction, is vital for appreciating their unique place in the animal kingdom. The longevity of their lives also provides a window into the importance of conservation efforts to protect them and their habitat. Their life cycle encompasses several key phases, including growth, reproduction, and the shedding of their exoskeleton, all of which are essential to their survival.
Moulting Process
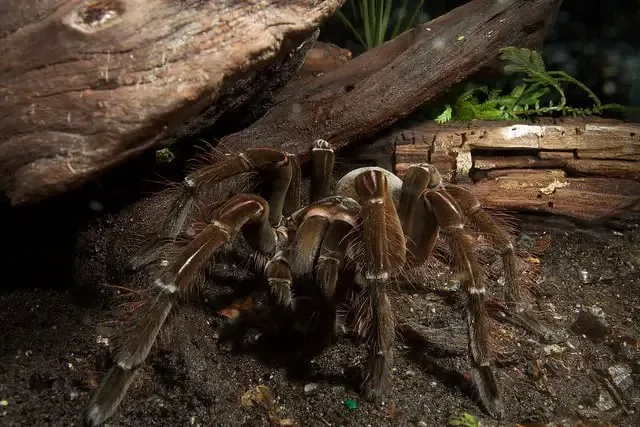

Like all tarantulas, Goliath Birdeaters grow by molting their exoskeleton. This process involves shedding their old outer layer to reveal a new, larger one. Molting is a vulnerable time for the spider. They are soft and defenseless during this period. The frequency of molting decreases as they mature. A healthy diet and environment are critical for their molting success. During the molting process, they are particularly susceptible to stress and harm. (Image goliath-birdeater-molting.webp)
Reproduction and Breeding
Reproduction in Goliath Birdeater Tarantulas involves a complex mating ritual. Males must approach the females cautiously to avoid being mistaken for prey. After mating, the female lays her eggs in a silken sac, which she fiercely protects. The spiderlings emerge from the eggs and go through several molts before reaching maturity. Breeding programs in captivity are often challenging and require careful management of environmental factors. Successfully breeding Goliath Birdeaters is an important step in conservation efforts.
Conservation Status and Threats
The Goliath Birdeater Tarantula faces various threats in its natural habitat, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts. Recognizing these threats helps in developing strategies to protect the species and its environment. Conservation efforts involve habitat preservation, sustainable practices, and awareness campaigns. Understanding the threats and the conservation efforts is crucial for ensuring the survival of this species for generations to come. Focusing on conservation not only helps these magnificent creatures but contributes to overall biodiversity.
Threats to Goliath Birdeater Populations

Habitat destruction is a significant threat to the Goliath Birdeater Tarantula. Deforestation, agricultural expansion, and mining activities reduce the availability of their natural habitat. They are also impacted by the pet trade, as they are often collected from the wild. Climate change and environmental degradation can also impact their survival. Addressing these threats requires a multi-faceted approach, including policy changes, community involvement, and scientific research.
Conservation Efforts
Various organizations and initiatives are working to protect the Goliath Birdeater Tarantula. These efforts include habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and captive breeding programs. Research on their biology and ecology also helps to inform conservation strategies. Education and awareness campaigns are also important to promote responsible interactions with wildlife and to highlight the importance of protecting their natural habitat. International cooperation and local community involvement are crucial for long-term success.
Amazing Facts
Goliath Birdeater Tarantulas are truly amazing creatures, and there are several fascinating facts that highlight their unique characteristics and behaviors. From their massive size to their hunting strategies and defense mechanisms, these spiders have captivated the interest of scientists and enthusiasts alike. Their ability to live in diverse environments and their complex life cycles make them a remarkable example of the wonders of nature. The more we learn about them, the more we appreciate their resilience and the importance of protecting their place in our world. (Image goliath-birdeater-eggs.webp)
